

1.- Longevity
2.- Cladode
3.- Acidity
Nutrious Used and Phisicologic effect of the ingest of the Nopal in the production of fecal Grounds
The Nopal is endemic of America and 258 grateful species exist, 100 of those are in Mexico who has an approximate surface of 10,000 Ha. of plantations specialized in Nopal for human consumption. Likewise, the Nopal can be an alternative cultivation for areas that are having problems for low yields due to the gradual impoverishment of the floors, or in places where there is deficiency of water for the traditional cultivations, being this, the case of the State of Nuevo León. México
In
Mexico is called Nopal to several species of the gender “Opuntia” of the family
“Cactaceae.”
In the book Cactáceas of Mexico of Helia Bravo(1978) for the Nopal it presents
2 gender Opuntia and Nopalea.
The gender Opuntia in Mexico presents 5 subgenus, 17 series and 104 species. The
gender Nopalea presents 10 species of those which the “Nopalea Cochenillifera”
it is used for human
consumption
In summary of the 104 species of Opuntia and 10 of Nopalea are used 15 for
forage, 5 for fruit and 3 for human consumption (2 of Opuntia and one of
Nopalea)
TAXONOMY
Reign Vegetable
Sub Reign Embryophita
Division Angioespermae
Class Dicotyledonous
Sub class Dialipetalas
Gender Opuntiales
Family Cactaceae
Sub family Opuntioideae
Tribe Opuntiae
Gender Opuntia
Opuntia Ficus Indica it hardly has thorns. It is an arborescent vegetable from 3 to 5 mt. of high, their trunk is woody and it measures of among 20 to 50 cm. of diameter. It forms oblong articles (Pencas or Cladodes) of 30 to 60 cm. of long x 20 to 40 cm. wide and of 2 to 3 cm. of thickness. Their branches are formed by pencas of opaque green color with areolas that contain yellow thorns more or less numerous, and it produces flowers from 7 to 10 cm of long, their fruit is oval of 5 to 10 cm. of long x 4 to 8 cm. of diameter and its color can be yellow, orange, red or purple with abundant fleshy and sweet pulp.
In appropriate lands with Neuter ph and without problem of plagues the Nopal can end up living up to 80 years. The commercial plantations of intensive exploitations, they can last 3 years.
The cladodes
(pencas) they transform the light in chemical energy through the photosynthesis,
they are recovered by a cuticle of the type lipidica, interrupted by the
presence of t estomas that they remain closed during the day.
The cuticle of the cladode avoids the dehydration
caused by the high temperatures of the summer. The normal hydrate of the cladode
reaches until 95% of water in weight.
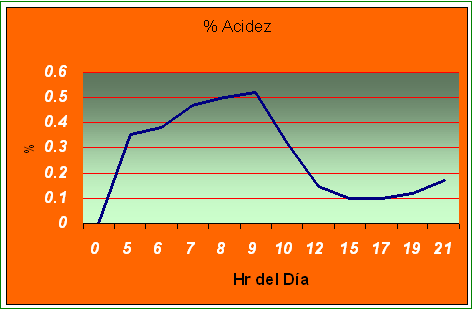
The acidity contained in the Nopal is determined in function of the hour in that it is harvested.
In 100 grs of Net weight of Nopal
|
CONCEPT |
CONTENT |
|
Energy (Kcal) |
78.00 |
|
Protein (gr.) |
27.00 |
|
Fatty (gr.) |
0.30 |
|
Carbohydrates (gr.) |
5.60 |
|
Calcium (mg.) |
93.00 |
|
Iron (mg.) |
1.60 |
|
Thiamine (mg.) |
0.03 |
|
Riboflavine (mg.) |
0.06 |
|
Niacine (mg.) |
0.03 |
|
Ascorbic acid (mg.) |
8.00 |
Bromatological Analysis Nopal Powder
|
CONCEPT |
METHOD |
RESULT |
|
FRESH |
DRY |
| Humidity | Gravimétric |
5.63% |
| Dry Matter | Diference |
94.37% |
| Ash | Gravimétric | 24.07 % |
| Ethereal Extract | Goldfisch | 2.04 % |
| Raw Fiber | Weende | 10.67 % |
| Protein | Kjeldhal | 7.53 % | |
| E.L.N. | Diference | 50.06 % | |
| Dietetic Fiber | 40.00% |
The analysis was made under the National Public Health laboratories recommended techniques
of the Secretaría de Salud ( Diciembre 2002 ) UANL Facultad de Ciencias Biológicas
% In 100 grs of Net weight of Nopal
|
AMINO ACID |
CONTENT |
|
Lysine |
4.00 |
|
Isoleucina |
4.00 |
|
Treonina |
4.80 |
|
Valina |
3.80 |
|
Leucina |
5.20 |
|
Triptófano |
0.80 |
|
Metionina |
0,70 |
|
Phenylalanine |
5.40 |
Nutritious use and Physiologic effect of the Ingest of the Nopal in the Production of Fecal Grounds
The Nopal have been a nutritious source in Mexico for hundred of years, at the moment also they have won popularity in the United States as much as vegetable for the case of the pencas, like of fruit for the case of the tunas. As vegetable you can use in Salads, Soups, Stews, Roasted, in short in a wide range of applications and the fruit is used mainly in sweet and jellies. It has been mentioned that the Nopal belongs to the gender “Opuntia” and one can say that all the species Opuntia are eatable from the moment in that they are NOT toxic. However, there are some species that are easier of using that others. And this rests basically in the content of thorns. The wild Nopal develop but quantity of thorns since this it is their means of survival, while the cultivated ones are improved species. The State of Texas in the United States mainly in Kingsville, has worked thoroughly in cultivating a variety without thorn that it contains less mucilage and resist low temperatures. Nevertheless, it has also been developed a lot of work about the mucilage like a dietary supplement to increase the ingest of soluble fiber the which it contributes several benefits to the health. The Nopal can eat up raw in salads, but most of people prefer them cooked and combined with other foods, as eggs, chili, shrimps, etc. and also in sauces. Recently it has been popularized the consumption of the Nopal liquefied cocktail with some Juice of Fruits. However, for some people they find a little bothersome the sensation that causes the mucilage (it Dribbles) that release the Nopal. The Powder of Nopal that is not another thing but that Dehydrated Nopal and Milled, it has come to offer a solution so much for this inconvenience, as well as for the elaboration of a wider range of such products as Breads, Cookies, Toasts, Tortillas, Etc.
PHYSIOLOGIC EFFECT OF THE INGEST OF NOPAL (1)
Although the Nopal is a food with a high grade of humidity, its fiber content in dry base is very important since its content as Total Dietary Fiber is bigger to 20% keeping a relationship 30:70 of soluble fiber to insoluble. Before this and their easy preparation for the human consumption rich foods can be developed in fiber like those mentioned in the previous paragraph, since they have been proven the benefits that it causes their consumption by means of investigations that relate the fiber consumption and the decrease of sufferings like colon cancer, arteriosclerosis, diabetes among others. Nevertheless, it is important to study the physiologic behavior of the fiber of the raw Nopal, since the tendency exists every time but marked for some years, of ingesting him in juice, blended with other fruits and vegetables with dietary ends to diminish of weight. The objective of the present study is:
1. - to elaborate diets balanced with different grade of substitution
of Nopal fiber
2. - To register the increase of weight, food ingest and production
of fecal grounds in rats Wistar during 14 days.
3. - To evaluate the physiologic answer based on the certain
parameters
4. - To identify a possible cause if there is loss of weight.
Materials and Methods
We worked with Nopal greenness (Opuntia Ficus Indica), it was cleaned perfectly, eliminating thorns and borders, it was cutted in uniform cubes of 1 cm. for side approx. those which they dried off in a dryer of fluidizes channel at 60°C until obtaining a smaller humidity to 6%. Later on they spent to a mill, until allowing that the obtained flour went by a mesh of 0.1 cm.
The Witness Diet was conformed according to the following balance:
|
Nutriment |
% |
Source |
| Carbohydrates |
60 |
Starch |
| Protein | 20 | Casein |
| Fiber | 5 | Cellulose |
| Vitamins | 1 | G.R Blend . |
| Mineral | 4 | Mezcla G.R. |
| Fatty | 10 | Corn Oil |
They thought about different test lots, having a diet balanced in nutritious, but with different fiber%
The test diets took raw Nopal to the 8, 11 and 15 fiber% each a respectively, reducing for it the quantity of carbohydrates. It was studied in rats female, young of the stump Wistar, the rats were distributed random mind in 4 lots, 5 rats each one, a rat for cage with consumption of water and food ad libitum.
The parameters of mensuration of the physiologic answer were:
Ø Initial Weight
Ø Ingestion of Food for rat per day
Ø Efficiency of conversion of the Food
Ø Fecal grounds in dry base per day
Ø Gr. of fecal grounds per day
Ø Gr. of food per kg of corporal weight
Ø Final Weight, gain in weight and ponderal increase of weight
Arithmetic mediate of each lot, once applied statistical analysis with their respective calculation of Standard Deviation
| Parameter | Witness | 8 % | 11 % | 15 % |
| Initial Weight (gr.) | 71.55 | 156.2 | 84.57 | 133.1 |
| Final Weight (gr.) | 136.5 | 176.5 | 85.16 | 131.6 |
| Weight Gain | 64.95 | 20.3 | 0.59 | -1.50 |
| Ponderal Increase (%) | 23.02 | 12.79 | 0.64 | -0.72 |
| Total Food Consume (gr) | 189.16 | 131.74 | 123.66 | 97.72 |
| Daily food Consumption(gr) | 13.51 | 9.41 | 8.83 | 6.98 |
| Conversion Ef (%) | 34.56 | 15.36 | 0.23 | -1.76 |
| Grounds per Day | 1.43 | 1.66 | 2.74 | 1.96 |
| (gr)Grounds/(gr. food/kg weight) | 1.04 | 1.14 | 2.08 | 2.27 |
Of these results it is observed that there is an important decrease of weight among the test groups when increasing the fiber content in their diet. If the ingestion of the food is compared, it is appreciated that there is a significant difference between the consumption of the group witness and those of test, especially, if one observes the group with the diet of 15 fiber%, however this result can be due to diverse reasons:
1. - that the food has not been of the total pleasure of the animals, with him
which a decrease of the consumption is caused
2. - that it has caused him a digestive uneasiness and they have associated it
with the consumed food Especially this last asception could have bigger
acceptance, since analyzing the production of fecal grounds, the test group
with 11% of fiber was the one that bigger quantity for day of fecal grounds
took place. Nevertheless, when establishing the relationship of grams of
fecal grounds taken place against the grams of food consumed among the
weight corporal livestock, it is seen that the group with 15 fiber% is that
of the index but high of produced fecal grounds.
CONCLUSIONS
1. - To bigger quantity of fiber in the diet, there is a remarkable production of
fecal grounds
2. - the consistency of the grounds fecal guard a narrow relationship with the
content of soluble fiber, making them viscous and not very
consistent for the great quantity of retained water.
3. - A significant loss of weight existed in the animals due to an excess of fiber
as well as to the type of present fiber in the Nopal.
4. - Signs and symptoms of malnutrition were presented due to the fiber
excess. These signs were of being expected if you observes that
there was a decrease in the grade of efficiency of conversion of the food, the
which it can be due to that some of the nutrients could not have had a
correct absorption for the organism when having been caught in the fiber
womb and to have been eliminated through the fecal grounds.
(1) Memories VII Congress National y V International about knowledge y utilization del Nopal
It has been demonstrated that the Nopal apart from its nutritional qualities, possesses medicinal properties that it help to control different you disorder of the such body as:
Nopal's 17 amino acids, 8 of which are essential and must be ingested as food, provide you with more energy and less fatigue by helping the body to lower blood sugar; elevate moods, suppress the appetite and provide nutrients. Fat build up is prevented, while fat break down and excretion is increased. Insoluble fibers such as Lignan is known for increasing satiety and eliminating excessive binges. Nopal's vegetable protein helps the body pull fluids from the tissues back into the bloodstream thereby diminishing cellulite and fluid retention.
Hiperglicemia (High Blood Sugar)
Nopal stabilizes and then regulates blood sugar by increasing the body's levels and sensitivity to insulin. Research studies have shown significant hypoglycemic effects maximal from 4 to 6 hours after Nopal ingestion in type II diabetics and non-diabetics. The dangerous side effects of high blood sugar levels including visual, blood vessel and nerve tissue disturbances are all addressed by Nopal's content of B-carotene (Vit. A ) Vitamin C, and Vitamins B1,2,3.
Hyperlipidemia (High cholesterol/ Fat levels):
Nopal's amino acids, fiber and B3 (niacin) prevent excess blood sugar conversions into fats, while reducing the total cholesterol, triglyceride and LDL cholesterol levels by metabolizing fat and fatty acids and eliminating excess bile acids (excess bile acid is eventually converted into cholesterol). Other research studies on B3 (niacin) show its conversion effects of LDL (bad) to HDL (good) forms of cholesterol and help decrease the risk of heart disease
Arteriosclerosis
The effects of the amino acids and fiber, including the anti-oxidant of Nopal's vitamin C and A (B-carotene) prevents the likelihood of blood vessel wall damage and the formation of fatty plaques.
Gastric Ulcers (Gastrointestinal Disorders)
Nopal vegetable fibers and mucilage's control excess gastric acid production and protect the Gastrointestinal mucosa. This pH buffering and coating has been studied for the prevention of damages that may occur from ingesting spicy foods, aspirin and other NSAIDs.
Digestion
Nopal's naturally available vitamins A, B1, 2, 3, C, minerals: Calcium, Magnesium, Sodium, Potassium, Iron, and Fibers in Lignin, Cellulose, Hemicelluloses, Pectin, Mucilage, and Gum form along with the 17 amino acids help to detoxify and support not only the liver but also the body in general. Ammonia, free radicals and environmental toxins such as alcohol and cigarette smoke-which all suppress the immune system are removed by Nopal. Nopal also aids in the balancing and calming of the nervous system, which benefits the body's overall function
Colon Cleansing
Nopal contains both soluble and insoluble dietary fibers. The insoluble dietary fiber in NOPAL (more commonly known as roughage), absorbs water and gently hastens food through the digestive track and contributes to regular bowel movements. In addition the presence of insoluble fibers in the colon help to dilute the concentration of potential carcinogens that may be present. Soluble fibers also contribute to regularity. Furthermore NOPAL is a gentle alternative to phylum for those with a sensitivity or allergy to phylum.